Could not find the Database Engine startup handle
PROBLEM
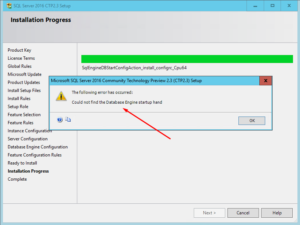
During SQL Server installation, you may run into the following error:
Could not find the Database Engine startup handle
The word handle is misspelled in the above screenshot. Microsoft should be excused because at the time I wrote this article, SQL Server 2016 was still in beta. The screenshots in this article are from SQL Server 2016 CTP2.3 running on Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview. I have experienced this error only in SQL Server 2016 CTP2.3 but you may also experience this error in SQL Server 2014 or 2008.
Here’s a solution that I found on Microsoft TechNet Wiki. There’s a lot more information in the wiki post. Here I am just documenting the steps in detail that I used to make the recommended change in the post.
SOLUTION
- 1. If you have installed SQL Server then you should remove it completely through the Control Panel and restart the server. If you need help, visit this wiki post for more information.
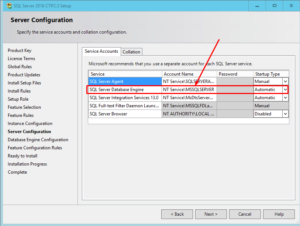
- 2. When you get to the Server Configuration page as shown below, you will notice that the SQL Server Database Engine service is using the account NT Service\MSSQLSERVER.
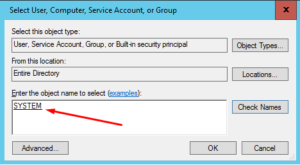
- 3. Change the account from NT Service\MSSQLSERVER to NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM by clicking on the drop-down box, selecting browse and then typing SYSTEM in Select User, Computer, Service Account, or Group window in Active Directory. Click OK to accept the new account.
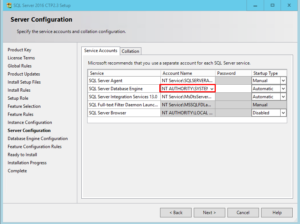
- 4. Your screen should look similar to the screenshot below.
- 5. Continue on with the installation as you normally would.
- 6. You should no longer receive the error Could not find the Database Engine startup handle during installation.
Best Practice: You should restart the Windows server after SQL Server installation is complete. Yes, even if you are not prompted by the system to restart the server you must restart the server after installation of SQL Server, SharePoint Server, etc. or else you may run into problems.
The wiki post recommends that after the installation is complete you should change this account back to a low-privileged domain account that will run the SQL Database Engine service. If you are still experiencing the error, please visit the wiki post because it has a lot more detail, references, links to forums, etc.
UPDATE: January 17, 2017
To change the account back to a low-privileged domain account, as mentioned above, follow the steps in this section. The domain account can be just a regular domain user account, not an administrator but it may need special permissions in SQL Server (not Windows Server, or Active Directory Domain). For example, the NT Service\MSSQLSERVICE and NT Service\SQLSERVERAGENT both have sysadmin permissions on the SQL Server by default, which means your domain account used as a service account will require these permissions on the SQL Server.
WARNING! You should only change the SQL Server service account if you are comfortable working with the SQL Server and understand how SQL Server account permissions work. If you are not sure what type of permissions are required for your SQL Server service account in your environment, I would recommend you don’t change the service account and contact a qualified SQL Server consultant or expert. Also, keep in mind that restarting the SQL Server means you are making the SQL Server unavailable until the service is started again. Although this is usually a short period, it is best that you perform this step outside of normal business hours.
- 1. Backup the SQL Server, including all databases.
- 2. Go to the SQL Server Configuration Manager.
- 3. Click SQL Server Services.
- 4. In the right-hand pane double-click SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER).
- 5. Click Browse and make sure the location is set to your domain, rather than your local SQL Server. If not, click Locations, select Entire Directory, and then click OK.
- 6. Type the name of the domain account that you want to use, click Check Names and then click OK.
- 7. Enter the password and then click OK.
- 8. You will be prompted to restart the SQL Server service. Click Yes to restart the service.
- 9. Your SQL Service account is now changed to a domain account.